Memory in Computer Systems
Role of Memory
In computers, memory is the most essential component of the normal functioning of any system. The computer system categorizes the memory for different purposes and uses.
Memory devices are digital systems that store data either temporarily or for a long term. Digital computers have built-in memory devices that can store the data of users or manufacturers.
The concept of memory and storage can be easily conflated as the same concept; however, there are some distinct and important differences. Memory is primary memory, while storage is secondary memory. Memory refers to the location of short-term data, while storage refers to the location of data stored on a long-term basis.
Classification of Memory
The following figure represents the classification of memory:
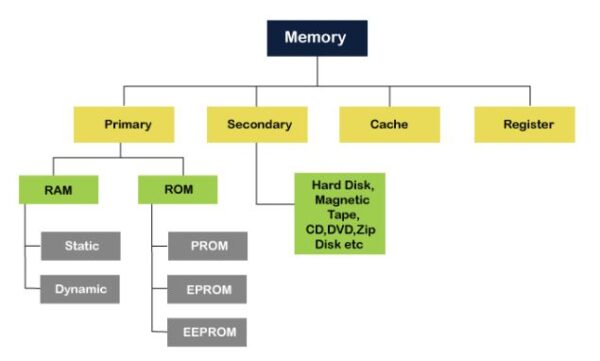
Primary or Main Memory
Primary memory is also known as the computer system’s main memory that communicates directly within the CPU, Auxiliary memory and the Cache memory. Main memory is used to kept programs or data when the processor is active to use them. When a program or data is activated to execute, the processor first loads instructions or programs from secondary memory into main memory, and then the processor starts execution. Accessing or executing of data from primary memory is faster because it has a cache or register memory that provides faster response, and it is located closer to the CPU. The primary memory is volatile, which means the data in memory can be lost if it is not saved when a power failure occurs. It is costlier than secondary memory, and the main memory capacity is limited as compared to secondary memory.
The primary memory is further divided into two parts:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read Only Memory)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
- SRAM
- DRAM
- It requires continuously refreshed to retain the data.
- It is slower than SRAM
- It holds a large amount of data
- It is the combination of capacitor and transistor
- It is less expensive as compared to SRAM
- Less power consumption
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
ROM is a memory device or storage medium that is used to permanently store information inside a chip. It is a read-only memory that can only read stored information, data or programs, but we cannot write or modify anything. A ROM contains some important instructions or program data that are required to start or boot a computer. It is a non-volatile memory; it means that the stored information cannot be lost even when the power is turned off or the system is shut down.
Types of ROM
There are five types of Read Only Memory:
- MROM (Masked Read Only Memory):
MROM is the oldest type of read-only memory whose program or data is pre-configured by the integrated circuit manufacture at the time of manufacturing. Therefore, a program or instruction stored within the MROM chip cannot be changed by the user. - PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory):
It is a type of digital read-only memory, in which the user can write any type of information or program only once. It means it is the empty PROM chip in which the user can write the desired content or program only once using the special PROM programmer or PROM burner device; after that, the data or instruction cannot be changed or erased. - EPROM (Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory):
It is the type of read only memory in which stored data can be erased and re-programmed only once in the EPROM memory. It is a non-volatile memory chip that holds data when there is no power supply and can also store data for a minimum of 10 to 20 years. In EPROM, if we want to erase any stored data and re-programmed it, first, we need to pass the ultraviolet light for 40 minutes to erase the data; after that, the data is re-created in EPROM. - EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory):
The EEROM is an electrically erasable and programmable read only memory used to erase stored data using a high voltage electrical charge and re-programmed it. It is also a non-volatile memory whose data cannot be erased or lost; even the power is turned off. In EEPROM, the stored data can be erased and reprogrammed up to 10 thousand times, and the data erase one byte at a time. - Flash ROM:
Flash memory is a non-volatile storage memory chip that can be written or programmed in small units called Block or Sector. Flash Memory is an EEPROM form of computer memory, and the contents or data cannot be lost when the power source is turned off. It is also used to transfer data between the computer and digital devices.
RAM vs ROM
| RAM | ROM |
|---|---|
| It is a Random-Access Memory | It is a Read Only Memory |
| Read and write operations can be performed | Only Read operation can be performed |
| Data can be lost in volatile memory when the power supply is turned off | Data cannot be lost in non-volatile memory when the power supply is turned off |
| It is a faster and expensive memory | It is a slower and less expensive memory |
| Storage data requires to be refreshed in RAM | Storage data does not need to be refreshed in ROM |
| The size of the chip is bigger than the ROM chip to store the data | The size of the chip is smaller than the RAM chip to store the same amount of data |
| Types of RAM: DRAM and SRAM | Types of ROM: MROM PROM EPROM EEPROM |