Best Python course in Pune
Welcome to Tech Amplifiers, the leading platform for best Python Training in Pune. Our Best Python course in Pune is designed to provide you with the essential skills and knowledge needed to excel in the world of coding. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced programmer, our Python course in pune offers a structured and comprehensive learning experience that will help you become proficient in Python. Join us today and unlock the potential of this versatile programming language
Featured Classes
INDUSTRY EXPERT
We have industry expert for your guidance
PRACTICAL ORIENTED
Practical knowledge is very important to understand how things actually work.
INSPIRING CLASSES
May you find great value in these inspirational Class
Features of Python Course
-

Overview
-
 Objective
Objective -
 Benefits for Students
Benefits for Students
Become a Python expert with our industry-leading Python course in Pune. Are you looking to enhance your programming skills and boost your career prospects?
Our comprehensive Python classes in Pune are the ideal choice for individuals who want to dive deep into the world of Python programming. Whether you’re searching for Python classes near me or an interactive Python online course, we have flexible options tailored to your needs.
With our course, you will gain a solid foundation in Python syntax, data structures, algorithms, and more. Our experienced instructors provide expert Python training in Pune, guiding you through hands-on exercises and real-world projects to ensure you develop a strong grasp of Python concepts.
What You Will Learn in Our Python Course
Our Python course in Pune is designed to provide you with the essential knowledge and practical skills needed to become a proficient Python programmer. Here’s what you will learn throughout the course:
- Python Basics: Build a strong foundation by understanding variables, data types, loops, and control structures in Python programming.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Explore OOP concepts, including classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism, to create modular and efficient code.
- Advanced Python Topics: Master advanced concepts such as file handling, exception handling, and working with regular expressions to solve real-world problems.
- Hands-On Experience: Work on practical, real-world projects to solidify your Python skills and demonstrate your expertise.
- Popular Python Libraries and Frameworks: Gain proficiency in widely-used libraries and frameworks for data analysis, web development, and beyond, ensuring you’re industry-ready.
Why Choose Our Python Course in Pune
When you enroll in our Python course in Pune, you gain access to a wealth of benefits designed to set you up for success:
- Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced industry professionals who bring real-world Python programming knowledge to the classroom.
- Hands-On Learning: Strengthen your skills with practical coding exercises, engaging quizzes, and real-world projects that prepare you for real-world scenarios.
- Personalized Guidance: Benefit from one-on-one attention and expert guidance to ensure you master Python concepts at your own pace.
- Industry-Aligned Curriculum: Stay ahead of the curve with a curriculum tailored to meet the ever-changing demands of the tech industry.
- Career Support: Take advantage of job placement assistance, career resources, and networking opportunities to launch your career in Python programming.
Python Course
- What is Python and history of Python?
- Why Python and where to use it?
- Discussion about Python 2 and Python 3
- Set up Python environment for development
- Demonstration on Python Installation
- Discuss about IDE’s like IDLE, Pycharm and Enthought Canopy
- Discussion about unique feature of Python
- Write first Python Program
- Start programming on interactive shell.
- Using Variables, Keywords
- Interactive and Programming techniques
- Comments and document interlude in Python
- Practical use cases using data analysis
- Introduction to Hadoop
- Python Core Objects and builtin functions
- Number Object and operations
- String Object and Operations
- List Object and Operations
- Tuple Object and operations
- Dictionary Object and operations
- Set object and operations
- Boolean Object and None Object
- Different data Structures, data processing
- What are conditional statements?
- How to use the indentations for defining if, else, elif block
- What are loops?
- How to control the loops
- How to iterate through the various object
- Sequence and iterable objects
- What are various type of functions
- Create UDF functions
- Parameterize UDF function, through named and unnamed parameters
- Defining and calling Function
- The anonymous Functions – Lambda Functions
- String Object functions
- List and Tuple Object functions
- Dictionary Object functions
- Process text files using Python
- Read/write and Append file object
- File object functions
- File pointer and seek the pointer
- Truncate the file content and append data
- File test operations using os.path
- Python inbuilt Modules
- os, sys, datetime, time, random, zip modules
- Create Python UDM – User Defined Modules
- Define PYTHONPATH
- Create Python Packages
- init File for package initialization
- Python Exceptions Handling
- What is Exception?
- Handling various exceptions using try….except…else
- Try-finally clause
- Argument of an Exception and create self exception class
- Python Standard Exceptions
- Raising an exceptions, User-Defined Exceptions
- Object oriented features
- Understand real world examples on OOP
- Implement Object oriented with Python
- Creating Classes and Objects, Destroying Objects
- Accessing attributes, Built-In Class Attributes
- Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Overriding Methods, Data Hiding
- Overloading Operators
- Debug Python programs using pdb debugger
- Pycharm Debugger
- Assert statement for debugging
- Testing with Python using UnitTest Framework
- What are regular expressions?
- The match and search Function
- Compile and matching
- Matching vs searching
- Search and Replace feature using RE
- Extended Regular Expressions
- Wildcard characters and work with them
- What are various type of functions
- Create UDF functions
- Parameterize UDF function, through named and unnamed parameters
- Defining and calling Function
- The anonymous Functions – Lambda Functions
- String Object functions
- List and Tuple Object functions
- Dictionary Object functions
- Process text files using Python
- Read/write and Append file object
- File object functions
- File pointer and seek the pointer
- Truncate the file content and append data
- File test operations using os.path
Python Foundation
- What is Python and history of Python?
- Why Python and where to use it?
- Discussion about Python 2 and Python 3
- Set up Python environment for development
- Demonstration on Python Installation
- Discuss about IDE’s like IDLE, Pycharm and Enthought Canopy
- Discussion about unique feature of Python
- Write first Python Program
- Start programming on interactive shell.
- Using Variables, Keywords
- Interactive and Programming techniques
- Comments and document interlude in Python
- Practical use cases using data analysis
- Introduction to Hadoop
Core Objects and Built-in Functions
- Python Core Objects and builtin functions
- Number Object and operations
- String Object and Operations
- List Object and Operations
- Tuple Object and operations
- Dictionary Object and operations
- Set object and operations
- Boolean Object and None Object
- Different data Structures, data processing
Conditional Statements and Loops
- What are conditional statements?
- How to use the indentations for defining if, else, elif block
- What are loops?
- How to control the loops
- How to iterate through the various object
- Sequence and iterable objects
UDF Functions and Object Functions
- What are various type of functions
- Create UDF functions
- Parameterize UDF function, through named and unnamed parameters
- Defining and calling Function
- The anonymous Functions – Lambda Functions
- String Object functions
- List and Tuple Object functions
- Dictionary Object functions
File Handling with Python
- Process text files using Python
- Read/write and Append file object
- File object functions
- File pointer and seek the pointer
- Truncate the file content and append data
- File test operations using os.path
Python Advance
- Python inbuilt Modules
- os, sys, datetime, time, random, zip modules
- Create Python UDM – User Defined Modules
- Define PYTHONPATH
- Create Python Packages
- init File for package initialization
Exceptional Handing and Object-Oriented Python
- Python Exceptions Handling
- What is Exception?
- Handling various exceptions using try….except…else
- Try-finally clause
- Argument of an Exception and create self exception class
- Python Standard Exceptions
- Raising an exceptions, User-Defined Exceptions
- Object oriented features
- Understand real world examples on OOP
- Implement Object oriented with Python
- Creating Classes and Objects, Destroying Objects
- Accessing attributes, Built-In Class Attributes
- Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Overriding Methods, Data Hiding
- Overloading Operators
Debugging, Framework & Regular expression
- Debug Python programs using pdb debugger
- Pycharm Debugger
- Assert statement for debugging
- Testing with Python using UnitTest Framework
- What are regular expressions?
- The match and search Function
- Compile and matching
- Matching vs searching
- Search and Replace feature using RE
- Extended Regular Expressions
- Wildcard characters and work with them
Database interaction with Python
- What are various type of functions
- Create UDF functions
- Parameterize UDF function, through named and unnamed parameters
- Defining and calling Function
- The anonymous Functions – Lambda Functions
- String Object functions
- List and Tuple Object functions
- Dictionary Object functions
Package Installation, Windows spreadsheet parsing and webpage scrapping
- Process text files using Python
- Read/write and Append file object
- File object functions
- File pointer and seek the pointer
- Truncate the file content and append data
- File test operations using os.path
What our Students say
FAQ'S
Python is a versatile and beginner-friendly programming language widely used in web development, data science, AI, ML, automation, and cybersecurity. Its simple syntax makes it easy to learn, and its high demand in the job market ensures excellent career opportunities. With strong community support and a vast collection of libraries, Python is ideal for both beginners and experienced developers. Enroll in the best Python course in Pune at Tech Amplifiers for hands-on training and 100% job placement
Python is a versatile, easy-to-learn programming language known for its simple syntax, readability, and flexibility. It is an interpreted and dynamically typed language, making debugging and development faster. With extensive libraries for AI, data science, web development, and automation, Python is widely used across industries. It supports object-oriented and functional programming, is platform-independent, and has a large community for support. Enroll in the best Python course in Pune at Tech Amplifiers to gain hands-on experience and secure 100% job placement.
To become a Python programmer, start by learning the fundamentals like syntax, variables, data types, and control structures. Move on to advanced concepts such as object-oriented programming (OOP), file handling, and libraries like NumPy and Pandas. Enroll in a Python training course in Pune to gain hands-on experience through real-world projects and certifications. Practice coding daily, contribute to open-source projects, and build a strong portfolio. Finally, apply for internships or jobs in web development, data science, or automation to kickstart your career.
Python Interview Questions for Freshers
- What is Python? What are the benefits of using Python
- What is a dynamically typed language?
- What is an Interpreted language?
- What is PEP 8 and why is it important?
- What is Scope in Python?
- What are lists and tuples? What is the key difference between the two?
- What are the common built-in data types in Python?
- What is pass in Python?
- What are modules and packages in Python?
- What are global, protected and private attributes in Python?
1. What is Python? What are the Benefits of Using Python Programming?
Python is a versatile, high-level programming language known for its simplicity, readability, and extensive applications in web development, data science, machine learning, and more.
Python’s ability to integrate with tools and libraries makes it ideal for building scalable, efficient solutions.
Benefits of Using Python:
- Ease of Learning and Readability: Python’s simple syntax reduces the learning curve and makes it easier to write and maintain programs.
- Versatility: With its support for third-party packages, Python enables modularity and reusability, making it a popular choice for scripting and automation.
- Rapid Application Development: Dynamic typing and built-in high-level data structures attract a large community of developers for rapid prototyping and deployment.
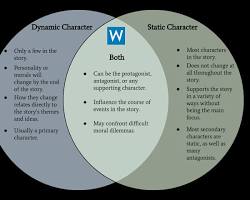
2.What Makes Python a Dynamically Typed Language?
In programming, typing refers to how data types are checked. Python is a dynamically typed language, meaning that type-checking occurs at runtime rather than during compilation.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Typing:
- Static Typing: Data types are checked before execution (e.g., C, Java).
- Dynamic Typing: Data types are checked during execution (e.g., Python, JavaScript).
Python’s dynamic typing enables flexibility, making it suitable for beginners and rapid prototyping. However, it requires careful handling to avoid runtime errors.
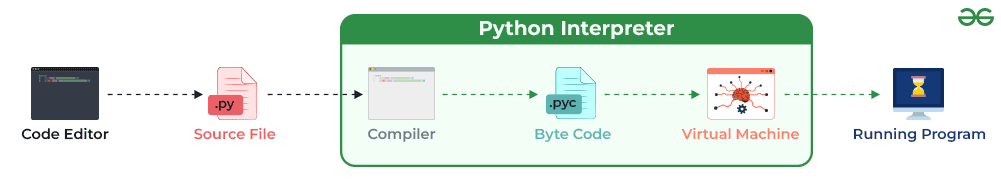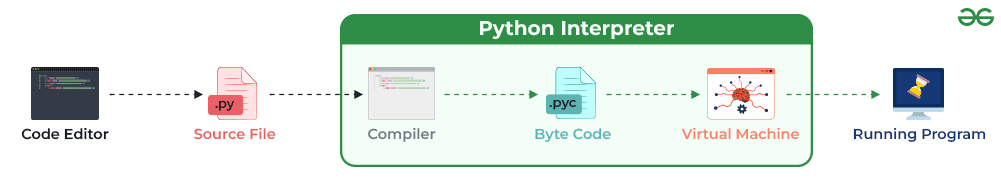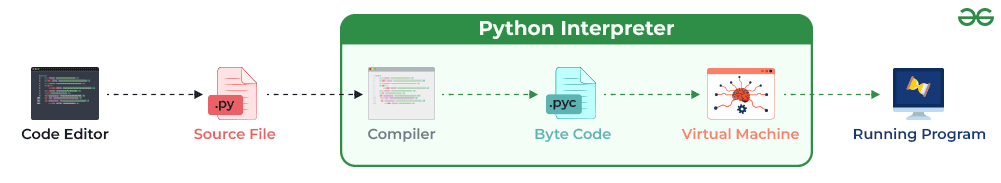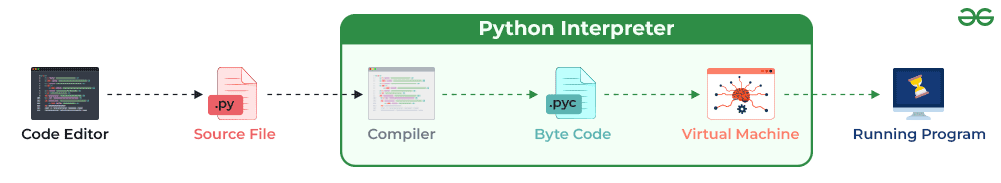
3. What is an Interpreted language?
An interpreted programming language executes code line by line, without requiring prior compilation. Python, JavaScript, PHP, and Ruby are prime examples of interpreted languages.
This feature makes Python ideal for:
- Debugging and testing.
- Scripting and automation tasks.
- Prototyping applications.
4. What is PEP 8, and Why Is It Essential in Python Programming?
PEP 8 is Python’s official style guide that outlines coding conventions for consistent and readable code.
Importance of PEP 8:
- Promotes code readability and maintainability.
- Standardizes contributions to open-source Python projects.
- Improves team collaboration by adhering to shared guidelines.
Key guidelines include:
- Using 4 spaces per indentation level.
- Limiting lines to 79 characters.
- Naming classes, functions, and variables using standard conventions.
5. What is Scope in Python?
In Python, every object operates within a defined scope, a block of code where the object remains relevant. Namespaces uniquely identify all objects within a program, and these namespaces have defined scopes where objects can be used without prefixes.
Examples of scope in Python include:
Local Scope: Refers to objects available within the current function.
Global Scope: Refers to objects available throughout the code execution from their inception.
Module-Level Scope: Refers to global objects within the current module accessible in the program.
Outermost Scope: Refers to all built-in names callable in the program, searched last to find referenced names.
Note: Local scope objects can be synchronized with global scope objects using keywords such as global.
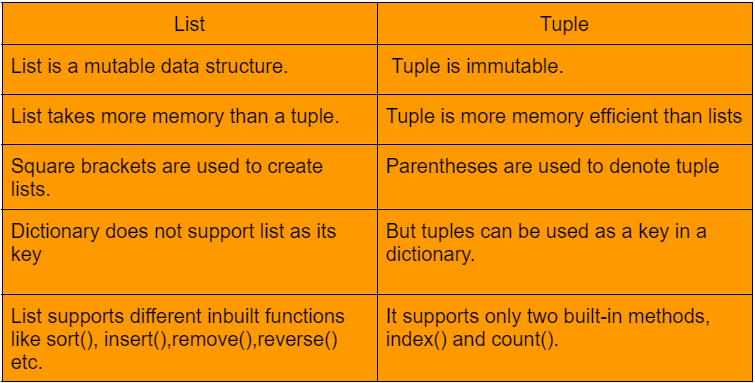
6. How Do Lists and Tuples Differ in Python?
Both lists and tuples are sequence data types in Python, used to store collections of objects.
Key Differences:
- Lists: Mutable and defined using square brackets (
[]). - Tuples: Immutable and defined using parentheses (
()).
Example:
python:
# List Example
my_list = [‘apple’, 2, 3.5]
my_list[0] = ‘banana’ # Allowed
# Tuple Example
my_tuple = (‘apple’, 2, 3.5)
my_tuple[0] = ‘banana’ # Throws an error
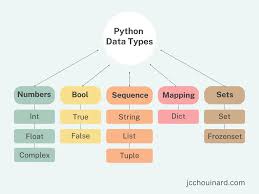
7. What are the common built-in data types in Python?
Python comes with a variety of built-in data types that can be used without explicit type declarations. While Python’s dynamic nature doesn’t require defining data types during variable declarations, it’s crucial to understand them to avoid type errors.
The type() and isinstance() functions can be used to check variable types. These data types fall into the following categories:
None Type:
NoneType: Represents null values in Python, indicated by the
Nonekeyword. Boolean equality operations can be performed on these objects.
Numeric Types:
There are three distinct numeric types, plus a subtype for booleans:
int: Stores integer literals, including hexadecimal, octal, and binary numbers.
float: Stores floating-point numbers, which include decimal values and exponential notation.
complex: Stores complex numbers in the form (A + Bj), with attributes
realandimag.bool: A subtype of integers, storing boolean values (
TrueorFalse).
Note: The standard library also provides fractions to store rational numbers and decimal for floating-point numbers with user-defined precision.
Sequence Types:
According to Python documentation, the three basic sequence types are lists, tuples, and range objects. These types support the in and not in operators for element traversal, sharing the same priority as comparison operations.
list: A mutable sequence used to store a collection of items.
tuple: An immutable sequence used to store a collection of items.
range: Represents an immutable sequence of numbers generated during execution.
str: An immutable sequence of Unicode code points to store textual data.
Note: Additional types for processing include binary data (bytearray, bytes, memoryview) and text strings (str).
Mapping Types:
Mapping objects map hashable values to arbitrary objects. They are mutable, and Python currently has one standard mapping type:
dict: Stores a comma-separated list of key-value pairs.
Set Types:
Python has two built-in set types:
set: A mutable unordered collection of distinct hashable objects, supporting methods like
add()andremove().frozenset: An immutable collection of distinct hashable objects, which cannot be modified after creation.
Note: The set type is mutable and cannot be used as a dictionary key. In contrast, the frozenset is immutable, hashable, and can be used as a dictionary key or as an element of another set.
Modules:
Modules are special built-in types supported by the Python interpreter. They support one special operation, attribute access (e.g., mymod.myobj), where mymod is a module and myobj references a name defined in the module’s symbol table.
The symbol table of the module resides in the special attribute __dict__, but direct assignment to this attribute is neither possible nor recommended.
Callable Types:
Callable types can be invoked with a function call. These include:
User-defined functions
Instance methods
Generator functions
Other built-in functions, methods, and classes
Why Choose Python Training in Pune with Tech Amplifiers?
- Why Python?
- What Makes Our Python Classes in Pune Unique?
- Why Choose Tech Amplifiers for Python Training?
1. Why Choose Python Training in Pune with Tech Amplifiers?
Selecting the right programming language to learn can be challenging, especially with so many options available. Whether you’re completing your studies or exploring courses to advance your career, choosing a technical course aligned with industry trends is crucial.
Among the various programming languages, Python stands out as a top choice due to its versatility and growing demand. If you’re looking to enhance your skills and boost your career, enrolling in Python training in Pune at Tech Amplifiers is the best decision you can make.
At Tech Amplifiers, we offer a structured and hands-on Python course in Pune that equips you with both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. While there are many Python training providers, Tech Amplifiers goes above and beyond by delivering a unique learning experience tailored to industry requirements.
2. Why Python?
Python is a beginner-friendly programming language and is ideal for anyone looking to step into the world of programming. Its simplicity and wide range of applications make it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced programmers.
Python is widely used in cutting-edge fields like Machine Learning, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, and Big Data. By mastering Python, you open the door to high-value career opportunities in these thriving industries.
3. What Makes Our Python Classes in Pune Unique?
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Learn everything from the basics of Python, including variables, data types, and control structures, to advanced topics like OOP concepts, threads, and modules.
- Expert Instructors: Our instructors at Tech Amplifiers are experienced IT professionals with in-depth industry knowledge, ensuring you learn from the best.
- Hands-On Learning: Gain practical experience through coding exercises, real-world projects, and hands-on training designed to prepare you for the demands of the IT world.
- Industry-Aligned Training: All sessions are conducted using the latest IT patterns, ensuring you’re prepared for highly sought-after Python proficiency.
- Certification: After completing our Python course, you will receive a recognized certification that is valued across the industry.
4. Why Choose Tech Amplifiers for Python Training?
While there are many institutions offering Python classes in Pune, Tech Amplifiers stands out by providing personalized guidance and career support. Here’s what sets us apart:
- Placement Assistance: Our Python training includes job placement support, helping you connect with top IT companies and secure your dream role.
- Modern Infrastructure: With state-of-the-art training centers located across Pune, we provide a comfortable and accessible learning environment.
- Customized Learning Paths: Whether you’re looking for Python classes near me or an interactive Python online course, we offer flexible options to suit your schedule.
Syllabus
Introduction
Social Engineering
Foot-printing
Vulnerability Assessment
Scanning
Enumeration
System Hacking
Malware Analysis
Sniffing
Session hijacking
Denial of Service
Web Server Hacking
Web Application Hacking
SQL Injection
Wireless network security
Mobile platform security
IDS, Firewall, Honeypot
Cloud computing
IoT Security
Cryptography
Online Python Classes
Python is a high-level programming language renowned for its dynamic semantics and versatility. This interpreted language is ideal for Rapid Application Development due to its built-in data structures that support dynamic typing and binding.
Python is also widely used as a scripting language to link together existing components efficiently.
One of Python’s most appealing features is its clean and simple syntax, making it easy to learn and use. Compared to other programming languages, coding and reading Python is much more straightforward, making it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced programmers.
If you’re looking to enhance your knowledge and skills in Python, join the Online Python Training offered by Tech Amplifiers. While there are many options for online Python classes in Pune, Tech Amplifiers stands out by providing a unique and comprehensive learning experience.
Unlock Python’s Potential
Python offers unparalleled opportunities in fields like web development, data analysis, and AI. Our Python programming course in Pune is designed to give you a competitive edge by covering key concepts, including:
- Classes and Objects
- Modules and Libraries
- Variables and Constructors
- Regular Expressions and Exception Handling
With Tech Amplifiers, you’ll not only learn Python but also gain the confidence to tackle real-world challenges and advance your career.
Enroll Now and Boost Your Career
Join our Python course in Pune at Tech Amplifiers and become part of an industry-leading training program. Whether you’re looking to learn Python for career advancement or personal growth, we provide the knowledge and support you need to succeed.
Don’t miss the chance to unlock high-value opportunities and take your programming skills to the next level.
Contact Tech Amplifiers today and start your journey toward becoming a certified Python programmer!
Explore Our Training Programs
Looking to upskill? Check out these industry-leading courses:
- Best Java Course in Pune– Master the art of Java programming with hands-on training.
- Best Angular Course in Pune – Become an expert in Angular and build dynamic web applications.
- Best React Course in Pune – Master the art of building dynamic user interfaces with React.
- Best IoT Course in Pune – Dive into the Internet of Things and learn how to connect the world.
- Best AI & ML Course in Pune – Explore Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning like a pro.
- Best AWS Course in Pune – Unlock the potential of Amazon Web Services for cloud computing.
- Best Cyber Security Course in Pune – Learn how to secure digital environments and safeguard data.